Hi, new followers! Seems like a good time for a re-introduction.
I'm Hong Minhee (洪 民憙), a software engineer based in Seoul. My pronouns are they/them.
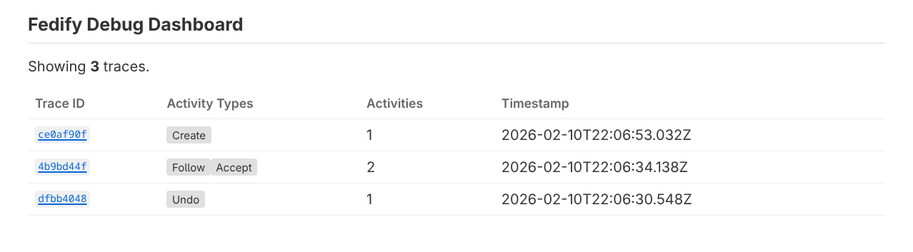
I build tools for the fediverse. Fedify is an ActivityPub server framework in TypeScript, Hollo is a single-user microblogging server (what you're reading this on), and BotKit is a framework for making ActivityPub bots. I care a lot about making federation more accessible to developers, which, as my recent JSON-LD rant probably made clear, sometimes means wrestling with parts of the spec I have complicated feelings about.
I'm a free/open source software person through and through, and a socialist, which informs how I think about tech. Lately I've been thinking a lot about LLMs. My position is probably not what you'd expect from either camp: I think the problem isn't the technology itself but the enclosure of the commons. I wrote about this at length here if you're curious: Histomat of F/OSS: We should reclaim LLMs, not reject them.
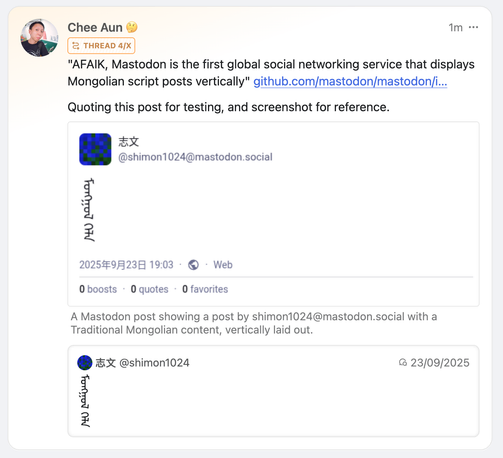
Outside of software, I have a long-running interest in CJK languages and writing systems. I'm always happy to talk about Chinese characters, Korean orthography, or the weird corners of Unicode where these things intersect.
Nice to meet you all, and thanks for following.